knowledge
Your current location:Home> Knowledge
Distinction between magnets, magnetic metals and non-magnetic metals(1)
As early as 2500 years ago, ancient civilization discovered the earliest magnets. In Europe and China in the 12th and 13th centuries, magnetic compasses were widely used in navigation.
Magnets play an important role in modern technology. With the increasing demand for magnetic circuit components widely used in industry, automobile, science and daily household equipment, the magnet product market continues to grow.
What is magnetism?
Magnetic force can be described as a force that attracts and repels magnetic objects. This force is mediated by a magnetic field penetrating different media. Some materials are inherently magnetic, which is a default property. However, some materials can be magnetized or demagnetized as required.
What substances in metals produce magnetism?
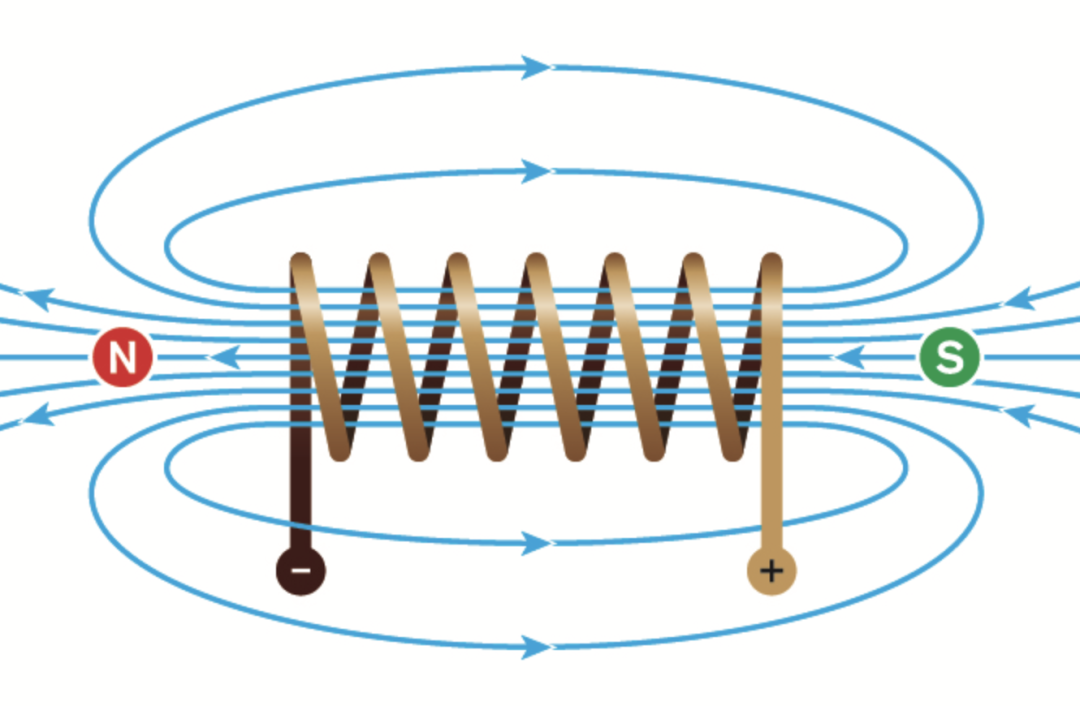
Magnetism is produced by the motion of electric charges. It is similar to current. When the charges spin, they produce a small dipole.
If the spins are balanced, the resultant force of these spins is negligible. On the other hand, if there are many unpaired electrons, the magnetic moment becomes very large. This process creates a magnetic field around the metal. Electric current can also produce a magnetic field. When a current passes through a wire, a circular magnetic field is generated around it. The magnetic field generated by the current near the conductor can also be used to generate current. Based on this principle, many innovative devices and applications using magnetism and electricity have been invented. Electromagnetic theory explains the progress of modern science and technology to a great extent.
Which magnets can be used There are many kinds of magnets. Magnetic metals can be distinguished by the time their properties remain active. Therefore, magnets can be divided into the following categories: Permanent magnet Temporary magnet electromagnet Permanent magnet When it comes to magnets, the first thing I think of is permanent magnets. Magnetizing these objects produces a magnetic field. Refrigerator stickers are a good example. They are usually pasted on the refrigerator door for hanging notes. Most permanent magnets contain iron, nickel, or cobalt. Permanent magnets are made of two types: "hard" magnets and "soft" magnets. "Hard" magnetic metals tend to remain magnetic for a long time. Here are some common examples: Alnico magnet is an alloy composed of aluminum, nickel and cobalt. Al Ni Co alloy can be used to make permanent strong magnets. It is widely used in consumer electronics and industry. For example, the material can be used in large motors, microphones, speakers, electric guitar pickups and microwave ovens. Ferrite is a ceramic compound composed of iron oxide and other elements (strontium or barium). Ferrite applications include refrigerator stickers and small motors. Neodymium iron boron magnet (NdFeB) is a rare earth magnet composed of neodymium, iron and boron alloys. It was invented by general motors and Sumitomo special metals in 1982. At present, the most powerful permanent magnet is neodymium magnet. Applications include wireless tools, hard drives, and magnetic fasteners. Samarium cobalt alloy is also a rare earth magnet, which is usually used in aerospace and other professional applications. "Soft" magnetic metals can also be magnetized, but soon lose their magnetism. Typical examples include ferrosilicon and ferronickel. Such materials are commonly used in electronic products, such as transformers and magnetic screens. The internal structure of a permanent magnet generates a magnetic field. They usually do not lose their magnetism easily. Ferromagnetic metals can be made into permanent magnets, and external influences will not make their magnetic fields disappear. They can withstand demagnetizing force, so they are relatively stable. The internal structure of magnet materials is the key to understand permanent magnets. When the magnetic domains of a material are arranged in the same direction, they will show magnetism externally. Magnetic domain is a small magnetic source in material structure. The magnetic domains of ferromagnetic materials are aligned in strong magnets. There are similar conditions inside the earth's core, so it is like a permanent magnet. But please note that the geographical North Pole of the earth is actually the magnetic south pole. Temporary magnet A temporary magnet is a magnet that acts the same as a permanent magnet in a magnetic field but loses its magnetism when it leaves the magnetic field. Under certain conditions, the temporary magnet can maintain its magnetism. If these conditions no longer exist, the magnetic field will disappear. Examples of temporary magnets include soft materials with low magnetism, such as annealed iron and steel. They become magnetic when placed in a strong magnetic field. Its force is low. Have you seen the paper clip near the permanent magnet? They stick together under the action of permanent magnets, which is their working mechanism. The magnetic field makes the paper clip a temporary magnet to attract other paper clips. When the permanent magnet is removed, the paper clip loses its magnetism. electromagnet When an electric current passes through, electromagnetism generates a magnetic field. Their applications are diversified. For example, electromagnets are used in motors, generators, relays, earphones, etc. The electromagnet consists of an iron core surrounded by a coil. By connecting the wire to the power supply, a strong magnetic field is generated. Using ferromagnetic materials, the strength of the magnetic field will be further expanded. Depending on the current, the electromagnet may have great strength. The magnetic force can also be turned on and off by pressing the button. Magnetic force has many special properties, so it can be used in a variety of applications. What are magnets made of A magnet is made up of a group of metals called ferromagnetic metals. For example, nickel and iron. This kind of metal is unique in its ability to magnetize uniformly. By asking how a magnet works, we mean how the magnetic field of a magnet acts on an object. The process of finding the answer is quite interesting. Each material contains several small magnetic fields called domains. More commonly, these domains are independent of each other and face different directions. However, when a strong magnetic field is applied, the magnetic domains of all ferromagnetic metals can be aligned, resulting in a stronger magnetic field. Most magnets are made in this way. Magnetic intensity Which magnets have the strongest magnetic force? Rare earth magnets are the most powerful magnets found so far. Among rare earth magnets, neodymium magnet has the strongest magnetic force. As long as the magnetic circuit is in good condition, samarium cobalt magnets can outperform new magnets at high temperatures (about 150 ° C or above). What are the factors that affect the strength of magnets? Magnet strength is affected by many factors, including: temperature radiation External magnetic field, e.g. high current Magnet close to another magnet (repulsion) Corrosion - some magnets require protective coatings to prevent corrosion in high humidity (e.g. NdFeB magnets) In modern magnet materials, impact and vibration have no effect unless the impact or vibration is strong enough to damage the magnet.